Generative AI is shifting the way we approach drug discovery. For years, finding new medicines was slow and expensive. Researchers had to sort through huge libraries of chemicals, spending millions of dollars and many years to develop just one drug. But now, with generative artificial intelligence, things are moving faster, easier, and at a lower cost.
One big success story is Insilico Medicine, which used AI to create a drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a rare lung disease. Traditionally, this would have taken six years and cost over $400 million. But with generative AI, they finished it in just two and a half years at one-tenth of the cost. This shows how cost-effective drug development can be with the help of advanced data science and machine learning.
The process involves using existing data to create new molecules through de novo drug design. This means designing drugs from scratch for specific diseases. These drug discovery applications are helping scientists identify potential medicines faster than ever before.
The market for generative AI in drug discovery is also growing exponentially. It’s expected to increase from $126.07 million in 2022 to $1.4 billion by 2032, growing at an impressive 27.38% annually.
In short, generative AI is revolutionizing drug discovery. This is just the beginning of a new era in healthcare.

Understanding How Generative AI Works in Drug Discovery
Gathering Data
The first step in GenAI’s approach to drug discovery is collecting data from various sources. This includes biological data (like genetics and protein structures), compound libraries (which contain data about chemical compounds), and clinical data (like patient medical records and trial results). The idea is to pull together as much relevant information as possible to make the drug discovery process smarter.
Key Data Sources Include:
- Biological Data: Genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data that help understand the molecular underpinnings of diseases.
- Compound Libraries: Collections of chemical compounds that may be tested for their ability to treat diseases.
- Clinical Data: Patient demographics, treatment outcomes, and data from clinical trials, providing real-world insights into drug effectiveness.
Organizing and Processing Data
Once the data is collected, it needs to be processed. This is where the real magic happens. Data goes through a series of transformations (like cleaning and organizing) to make it ready for analysis. Essentially, this helps AI models understand and interpret the data accurately. This structured data is then stored in what’s called a vector database, which allows the system to search, compare, and retrieve information quickly.
Using AI for Deep Insights
After the data is organized, AI models—specifically Large Language Models (LLMs)—come into play. These models process the data by turning it into a format (called vectors) that AI systems can easily work with. Once that’s done, the AI uses these vectors to answer complex questions, like which compounds might work best for a disease or how safe a potential drug is.
How AI Helps in Drug Discovery:
- Speeding up research: GenAI can analyze vast amounts of data far quicker than traditional methods.
- Identifying new drug targets: AI can sift through data to find potential new targets for drugs, which could lead to breakthroughs.
- Predicting drug effectiveness and side effects: AI models predict how drugs will behave in the body, helping to identify issues early on.
Decision Making and Insights
Once the AI has done its thing, it provides outputs in the form of detailed reports. These reports could highlight things like:
- Possible side effects of a compound
- Effectiveness in treating specific diseases
- Suggestions for improving a drug’s structure
These insights are then presented on a drug discovery platform, a tool that helps researchers and companies make better, data-driven decisions.
Key Phases of Generative AI in Drug Discovery
1. Target Identification
The first step in developing any new drug is to figure out which biological “target” the drug should focus on. These targets are usually proteins or genes linked to diseases. Finding the right target is crucial because it’s the foundation for creating an effective drug.
How AI Helps:
- AI models analyze vast amounts of biological data (like genetic sequences and protein structures).
- It helps scientists identify potential targets faster than traditional methods, uncovering hidden patterns that might be overlooked.
AI can spot relationships between diseases and molecular targets, offering new ideas for what to target with a drug.
2. Drug Design & Molecule Generation
Once a target is identified, the next step is designing a drug that can interact with it. This is where AI shines. AI systems can create entirely new molecules that could work as potential drugs. These molecules are designed to fit perfectly with the target, just like a key fits into a lock.
How AI Helps:
- AI looks at millions of different chemical compounds to find the ones that could work best.
- It uses data from compound libraries (databases of chemical compounds) to generate new molecules with the desired properties.
This helps speed up the drug design process, cutting down on trial and error, and improving the chances of success.
3. Optimization
After designing a drug, the next challenge is to make sure it works well inside the body. This includes making sure it’s absorbed properly, reaches the right places, and has the desired effect. AI is used to optimize these properties to improve the drug’s performance.
How AI Helps:
- AI analyzes the molecular structure and predicts how the drug will behave in the body.
- It can suggest changes to improve things like bioavailability (how well the body absorbs the drug) and efficacy (how well it works against the disease).
AI speeds up the optimization process, allowing researchers to find the best versions of a drug much quicker.
4. Preclinical and Clinical Trials
Before a new drug can be given to patients, it has to go through extensive testing in preclinical studies (usually in labs or with animals) and clinical trials (with humans). AI can play a role in both.
How AI Helps:
- Preclinical Trials: AI can help design experiments and predict outcomes, which helps avoid wasting time and resources.
- Clinical Trials: AI is used to design better trial protocols, predict which patients might respond best to the drug, and even monitor trial results in real-time. This can lead to more successful trials and faster approval.
Benefits of Using Generative AI in Drug Discovery
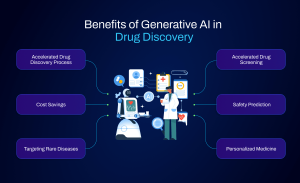
1. Faster Drug Discovery Timelines
Traditionally, it could take over a decade to bring a new drug to market. With generative AI, this timeline is being cut down drastically. AI helps streamline many steps in the drug discovery process, making things move faster.
Real-life Example:
- Insilico Medicine, a biotech company, used generative AI to develop a drug called INS018_055, which reached Phase 1 trials in just 30 months. Normally, this process could take up to 7 years using traditional methods.
By speeding things up, AI is helping get life-saving drugs to patients much faster.
2. Cost Efficiency in R&D
Drug discovery and development are expensive. On average, big pharmaceutical companies spend around $6.16 billion to develop a single drug. But with generative AI, companies are able to cut these costs significantly.
How AI Helps:
- It automates repetitive tasks, improves data analysis, and helps researchers make smarter decisions, all of which save time and money.
- Insilico Medicine, for example, spent only a fraction of the usual amount (one-tenth) to advance its drug to Phase 2 trials.
With AI handling much of the heavy lifting, R&D expenses are going down.
3. Increased Precision and Accuracy in Drug Design
When designing new drugs, precision is key. Even small changes in a drug’s structure can make a huge difference in its effectiveness. Generative AI makes it possible to design drugs with higher precision and accuracy, ensuring they work as intended.
How AI Helps:
- AI systems analyze huge amounts of biological and chemical data to predict how a drug will behave in the body.
- It helps scientists design molecules that are more likely to interact with specific targets in a precise way.
This means drugs can be tailored more accurately to treat diseases, improving their chances of success.
4. Exploring Vast Chemical Space for Novel Drug Candidates
There are billions of potential molecules that could become effective drugs, but it’s impossible for humans to manually explore them all. AI can sift through this “chemical space” and identify promising candidates much more quickly than traditional methods.
How AI Helps:
- AI generates and tests a vast array of new molecular structures, some of which may not have been considered before.
- This opens up new possibilities for finding drugs that could work for diseases that have been hard to treat.
With AI, the potential for discovering novel drug candidates is almost limitless.
5. Enhanced Ability to Predict Drug Success
One of the biggest challenges in drug development is predicting which drugs will succeed in clinical trials. Around 90% of drugs fail at this stage. AI can help predict whether a drug will work in real-world trials, saving time and money by avoiding drugs that are unlikely to succeed.
How AI Helps:
- AI tools like inClinico are being used to predict the outcomes of clinical trials with high accuracy. In a 7-year study, this AI tool correctly predicted clinical trial outcomes 79% of the time.
- This helps researchers focus on the most promising candidates and avoid wasting resources on drugs that are unlikely to work.
Key Use Cases of Generative AI in Drug Discovery
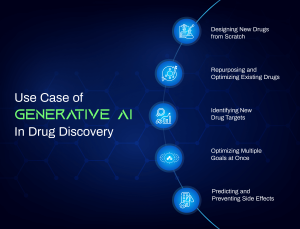
Designing New Drugs from Scratch
Imagine drawing up a dream drug with specific attributes like high efficacy and fewer side effects—and having AI create it for you!
- Generative AI studies existing molecules and their properties.
- Using tools like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), it generates entirely new molecules that meet desired criteria.
- For instance, in Parkinson’s disease research, AI can design molecules that cross the blood-brain barrier and stabilize neurons, making therapies more effective and tolerable.
Repurposing and Optimizing Existing Drugs
Generative AI doesn’t just create new drugs—it can also breathe new life into existing ones.
- Drug Repurposing: AI analyzes how a current drug might work for a different disease.
- Optimization: It suggests tweaks to a molecule’s structure to improve things like solubility or stability while keeping its effectiveness intact.
Example: Virtual simulations allow researchers to test these modifications on “digital patients,” saving time, money, and reducing risks.
Identifying New Drug Targets
AI digs through complex biological data to find hidden opportunities for precision medicine.
- It examines genomic and proteomic data to uncover biomarkers or genetic variations linked to diseases.
- These insights allow researchers to create drugs that work on very specific disease mechanisms.
Example: For prostate cancer, AI helped develop drugs targeting androgen receptors, effectively slowing cancer growth.
Optimizing Multiple Goals at Once
Drug discovery often requires balancing multiple objectives, like maximizing efficacy while minimizing side effects.
- Generative algorithms use techniques like reinforcement learning and evolutionary algorithms to fine-tune drug properties.
- For example, AI helps design controlled-release formulations that regulate how a drug is absorbed by the body, improving patient outcomes.
Predicting and Preventing Side Effects
One of the biggest challenges in drug development is identifying harmful side effects early.
- Generative AI can analyze patient genetic data, historical drug outcomes, and other data to predict potential adverse reactions.
- This allows pharmaceutical companies to modify risky compounds before trials and helps doctors personalize treatment plans.
Example: AI flagged genetic markers linked to liver toxicity, enabling safer drug design.
Traditional Drug Discovery vs. Generative AI-Powered Drug Discovery

Process
- Traditional drug discovery follows a sequential approach, where every step—from identifying a target to testing potential compounds—happens one after the other.
- Generative AI, on the other hand, works in an iterative process. It uses algorithms to analyze data, generate molecules, and refine them continuously based on feedback.
Effort
- The traditional method is labor-intensive, with researchers manually designing experiments and testing compounds over a long time.
- Generative AI makes this process data-driven and automated, allowing machines to handle molecule generation, trial protocols, and even predicting success rates.
Timeline
- Traditional methods take years to complete, with lengthy lab work and multiple trial phases.
- With Generative AI, timelines can shrink dramatically, often cutting the process down to a third of the usual time.
Cost
- Traditional drug discovery is incredibly expensive, costing pharmaceutical companies billions of dollars.
- Generative AI offers a cost-effective alternative, delivering similar results at a fraction—sometimes one-tenth—of the cost.
Data Integration
- Traditional methods rely on limited data, mostly from experiments and existing compounds.
- Generative AI leverages large datasets, including genomics, clinical records, chemical properties, and even published research, to create better drug candidates.
Target Selection
- In traditional drug discovery, researchers often stick to known targets and predetermined pathways.
- Generative AI expands possibilities by identifying new, alternative targets for testing and development.
Personalization
- Traditional drugs are generally designed for the general population, offering limited personalization.
- Generative AI uses patient-specific data, such as biomarkers, to design drugs tailored to individual needs, paving the way for personalized medicine.
Tap into our expert talent pool to build cutting-edge AI solutions.
Real-Life Examples of Generative AI in Drug Discovery
Adaptyv Bio: Better Protein Engineering
A biotech startup in Switzerland, Adaptyv Bio, is using generative AI to create proteins. Their AI doesn’t just stop at designing; it also helps write lab plans and produces the proteins. This means scientists can focus more on breakthroughs and less on repetitive tasks.
Insilico Medicine’s PandaOmics
Insilico Medicine developed a tool called PandaOmics that uses AI to find drug targets and biomarkers. For example, they’ve identified markers for diseases like gallbladder cancer and even hair loss. This helps researchers figure out where to focus their treatments.
MIT and Tufts’ ConPLex: Speedy Screening
At MIT and Tufts, researchers created ConPLex, an AI that evaluates how drugs interact with target proteins. This tool screened over 100 million compounds in just one day. It found 19 good matches, and 12 of them were so effective they needed only tiny amounts to work.
Alzheimer’s Research with AI
Generative AI is helping in the fight against Alzheimer’s. Scientists used it to analyze existing drugs and found 20 that might help. After testing, three—metformin, losartan, and simvastatin—showed promise in reducing Alzheimer’s risks in older adults.
IBM’s Dementia Discovery
IBM used AI to explore medications for dementia linked to Parkinson’s. The AI suggested repurposing two drugs: rasagiline (used for Parkinson’s) and zolpidem (a sleep aid). By analyzing data from different patient groups, the AI uncovered new possibilities for treatment.
Fighting Superbugs
Researchers from Stanford and McMaster tackled antibiotic-resistant bacteria (Acinetobacter baumannii). They used AI to generate billions of possible molecules, then narrowed it down to six strong candidates. This is a big step in the fight against deadly, drug-resistant infections.
AlphaFold’s Quick Win
AlphaFold, an AI tool for predicting protein shapes, helped researchers discover a new molecule to fight cancer (a CDK20 inhibitor). It only took 30 days to find, compared to months or even years using older methods.
Evotec and Exscientia: Cancer Treatment in Record Time
These two companies teamed up and used AI to develop a cancer drug in just eight months. Normally, this process can take four to five years. The drug is now in clinical trials, showing how AI can speed things up without cutting corners.
Conclusion
Generative AI is proving to be a game-changer in drug discovery, transforming how new medicines are developed. With its ability to use model development and advanced algorithms, it speeds up the process, reduces costs, and enhances precision in finding effective treatments.
As this technology continues to evolve, generative AI drug discovery holds immense potential to reshape the future of healthcare, making innovative solutions more accessible and efficient for everyone.
Transform Your Drug Discovery with AI – Work with Wow Labz Today!
At Wow Labz, we specialize in using advanced AI technology to help improve the process of discovering new medicines. We have worked with top experts in the field to create AI tools that make drug discovery faster, more accurate, and more cost-effective. From predicting how molecules will behave to designing entirely new drug candidates, our solutions are changing the way pharmaceutical research is done.
We’ve already made a significant impact in drug discovery by helping companies reduce the time and money spent on experiments, predict potential issues earlier in the process, and improve the chances of developing successful drugs.
If you’re looking for ways to speed up your research, improve your drug development, or discover new medical treatments, Wow Labz is the partner you need. We’d love to work with you to take your research to the next level and help bring groundbreaking medicines to market. Get in touch with us today to find out how we can help make your drug discovery process smarter and faster!