AI agents in HR are becoming a key part of how companies manage people and processes. According to Salesforce, AI agent adoption is expected to grow by 327% in just two years, resulting in a 30% increase in productivity. As more companies turn to digital labor, HR leaders are starting to rethink how roles are structured and what skills are needed. The study found that nearly 25% of the workforce may be redeployed as these changes take place.
To stay prepared, more than 80% of HR leaders are investing in reskilling programs to help employees adapt. They believe the future will include both humans and AI agents working together. But many companies haven’t started yet, 85% haven’t implemented agentic AI, and 73% of employees still aren’t sure how it will affect their roles. With this shift coming quickly, understanding how HR is planning for it matters more than ever.
Understanding AI Agents in HR and Their Key Capabilities
Major Capabilities of AI Agents in HR
- Understands text and speech
Can communicate with candidates or employees in natural language—both written and spoken.
- Plans tasks and executes them
Can schedule interviews, send follow-ups, and run surveys without manual input.
- Remembers past actions and context
Uses employee history or previous conversations to respond more accurately.
- Connects to other systems
Links with emails, HRMS platforms, calendars, and job boards to complete tasks across tools.
- Learns from feedback
Improves performance by learning from past results and feedback, gets smarter over time.
Key Components of AI Agents in HR
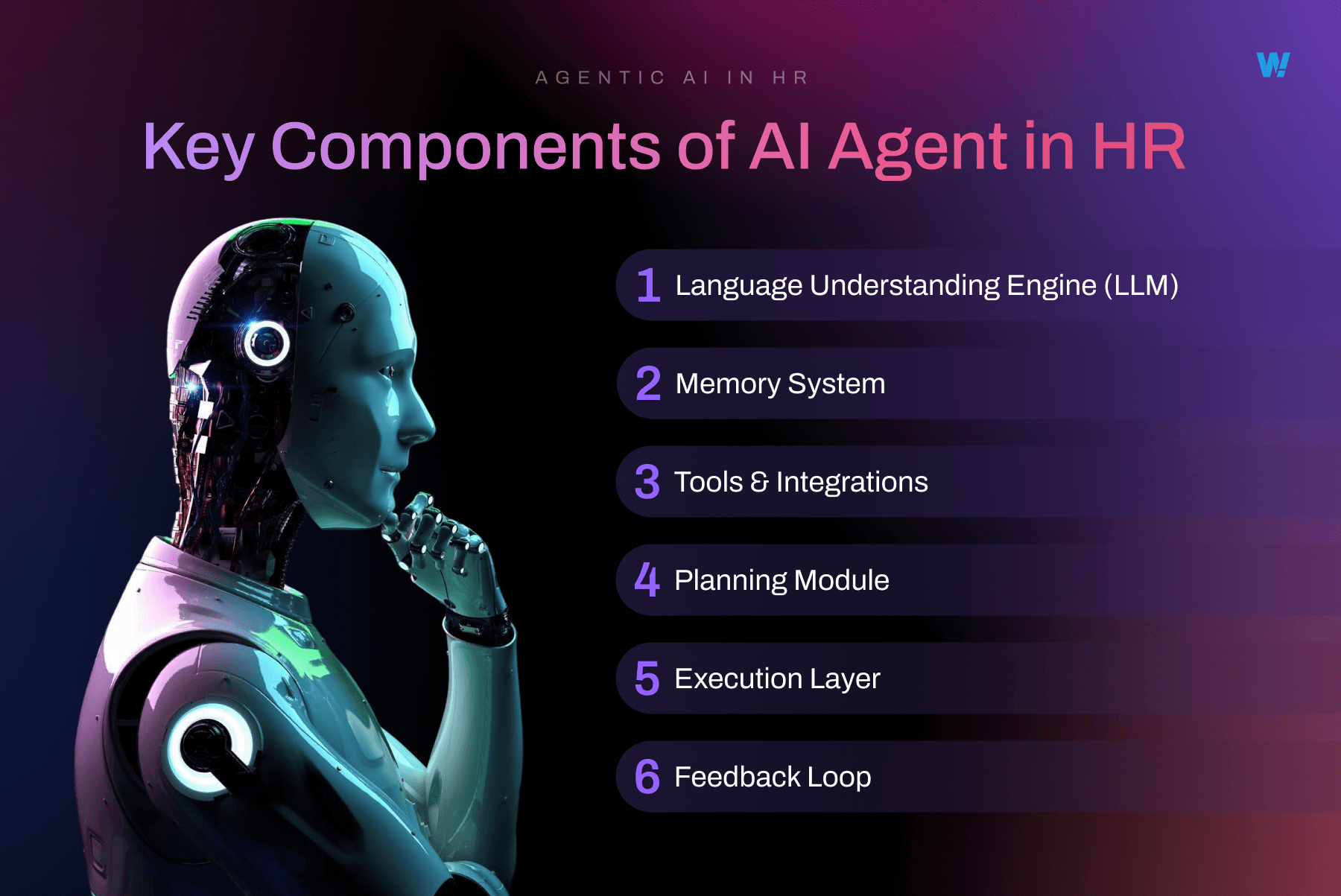
AI agents in HR are built with several core components that work together to support day-to-day HR functions. These components allow them to take on tasks, respond intelligently, and support both employees and HR teams across the entire employee journey.
Here’s a closer look at each component, explained with examples relevant to HR operations.
1. Language Understanding Engine (LLM)
This is the part of the AI agent that allows it to read, understand, and respond in human language. It’s usually powered by a large language model (LLM) that has been trained on a wide range of information.
In the context of AI in HR, this component helps with:
- Resume screening: The agent can read hundreds of CVs and identify relevant experience, skills, and qualifications without human input.
- Policy explanation: It can answer employee questions like “How many sick leaves do I have left?” or “What’s the company policy on remote work?” clearly and accurately.
- Content generation: HR teams can ask the agent to draft job descriptions, onboarding messages, or internal announcements.
2. Memory System
The memory system enables the agent to remember what it has done before—conversations, data, and tasks. Unlike chatbots that forget every time a new session starts, AI agents retain useful context.
For example:
- If a candidate asks a question during recruitment and returns a week later, the agent can pick up the conversation without starting from scratch.
- For employees, the agent can recall previous requests, such as leave applications or updates to employee records.
- It also remembers preferences and actions of HR professionals, offering better assistance over time.
3. Tools and Integrations
AI agents become far more effective when they are connected to the tools your HR department already uses. These include both internal and external platforms.
Examples of integration in HR processes:
- Email (Gmail/Outlook): Sending follow-up messages to candidates or reminders to employees.
- Slack or Teams: Answering real-time queries or pushing important HR notifications.
- Applicant Tracking System (ATS): Reviewing job applications, tracking candidate stages, or updating status after interviews.
- HRMS platforms: Accessing and updating employee data, handling payroll entries, or managing leave balances.
- Notion or other wikis: Fetching policy details or HR documentation to share with employees.
With these integrations, AI agents in HR can complete full workflows instead of doing one-off tasks. This removes friction and reduces manual switching between tools.
4. Planning Module
The planning module allows the AI agent to map out how to achieve a goal. Instead of just responding to a command, it thinks through the steps needed to deliver a result.
Let’s take a few HR examples:
If the goal is to hire a software engineer, the agent can break it down into sub-tasks:
- Post the job description
- Screen applications
- Schedule interviews
- Follow up with candidates
If the goal is employee onboarding, the steps might include:
- Sending welcome emails
- Assigning documents and forms
- Booking a training session
5. Execution Layer
Once a plan is made, the execution layer puts it into action. This is where the AI agent performs the actual work involved in HR processes.
In practical terms, this could mean:
- Sending invitations to shortlisted candidates
- Filing documents in the appropriate HR system
- Assigning learning modules based on role or performance history
- Updating compliance logs or payroll entries automatically
6. Feedback Loop
A good AI agent doesn’t just complete tasks, it also learns and improves with experience.
This component is responsible for:
- Analysing outcomes (e.g., whether a candidate accepted an offer or dropped off)
- Adjusting how it handles similar tasks in future
- Identifying patterns and sharing insights with HR professionals
For example, if candidates often ignore a particular type of follow-up message, the agent can recommend or switch to a better-performing approach. Similarly, it can help HR teams refine performance management strategies or improve internal communication practices.
Use Cases of AI Agents in HR
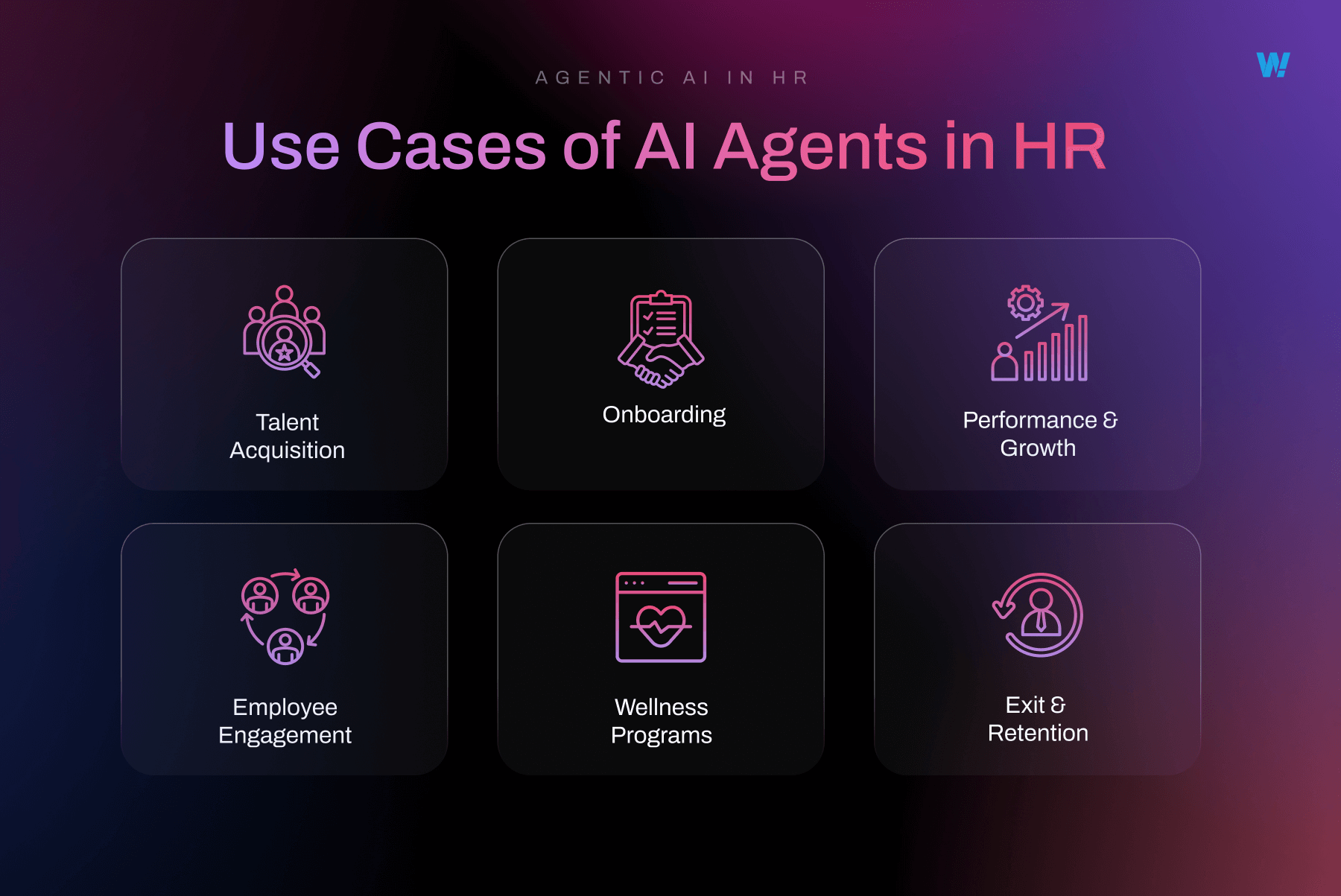
a. Talent Acquisition
AI agents play a vital role in improving hiring speed and accuracy. They help HR departments manage large volumes of applicants without losing quality or consistency.
- Resume Parsing and Ranking
The agent scans resumes to extract key data like education, skills, certifications, and past job roles. It matches candidates to job descriptions using smart filters and prioritises the most suitable ones. This helps recruiters avoid manual shortlisting and speeds up the recruitment process.
- Personalised Candidate Outreach
Based on candidate profiles, the agent drafts and sends tailored messages that match the tone and role—improving response rates. It can also follow up automatically if no reply is received.
- Interview Scheduling and Coordination
The agent finds suitable time slots based on the interviewer’s and candidate’s calendars, books the meeting, sends out invites, and shares reminders. It can also reschedule if someone cancels. This removes constant back-and-forth coordination from HR teams.
b. Onboarding
First impressions matter. AI in HR makes onboarding faster, smoother, and more engaging for new hires.
- Interactive Welcome Agents for New Hires
AI agents greet new employees through chat, walk them through the onboarding journey, and offer guidance on what to expect in the first week. This builds early confidence and reduces uncertainty.
- FAQ Assistants for Tools, Policies, and Teams
Instead of contacting HR for every small question, new employees can ask the AI agent. It provides accurate answers on topics like leave, internal tools, team structures, and more. This reduces the burden on HR professionals and ensures quick access to information.
- Setting Up Meetings, Accounts, and First Tasks
The agent coordinates with IT to set up emails and access. It also schedules intro meetings, assigns onboarding tasks, and tracks completion. This improves onboarding compliance and ensures no step is missed.
c. Performance & Growth
Performance and employee development often involve tracking goals, reviewing feedback, and recommending learning paths. AI agents support this efficiently and consistently.
- Track Goals and Check-ins
AI agents maintain a log of individual and team goals, remind managers and employees about upcoming check-ins, and flag overdue updates. They also help prepare reports for review cycles.
- Suggest Training Programmes Based on Role or Feedback
By analysing performance reviews, skill gaps, and job roles, the agent can recommend personalised training courses or learning resources. This supports continuous learning aligned with company needs.
- Analyse Sentiment from Performance Reviews
Using natural language understanding, AI agents evaluate written reviews to detect positive, neutral, or negative sentiment. This helps HR leaders understand morale and coaching needs across departments.
d. Employee Engagement
Maintaining engagement is key to reducing attrition and increasing satisfaction. AI agents offer proactive tools to support engagement without creating survey fatigue.
- Run Quick Pulse Surveys
The agent sends brief surveys via chat or email to gather feedback on workload, team dynamics, and satisfaction. It automatically compiles and visualises the results for the HR department to act on.
- Monitor Team Mood via Communication Tone
With permission, the AI can assess tone and emotion in written communication (e.g., Slack messages) to detect stress, disengagement, or burnout. It flags early signs for HR to follow up.
- Recommend Team-Building Initiatives
Based on survey feedback or communication patterns, the agent can suggest activities like team games, workshops, or recognition programmes to improve team cohesion.
e. Wellness Programmes
Supporting mental and physical health is now a key part of HR operations. AI agents provide quiet, consistent help in this space.
- Mental Health Check-ins Through Chat
The agent checks in with employees periodically to ask how they’re feeling. These conversations can be private, non-judgemental, and used to guide people to the right support resources.
- Nudges for Breaks, Fitness Sessions, Mindfulness
Based on work hours, meeting loads, and activity, the AI agent sends reminders to take breaks, stretch, join a wellness session, or try mindfulness. This helps prevent burnout.
- Personalised Wellness Resource Suggestions
Depending on the person’s role, activity, or interest, the agent can recommend articles, workshops, or benefits related to mental wellbeing, exercise, or stress management.
f. Exit & Retention
Understanding why employees leave—and preventing avoidable exits—is a major concern for HR professionals. AI agents help gather insights and support timely action.
- Proactively Detect Signs of Disengagement
The agent monitors changes in communication, missed check-ins, or lack of participation in team activities. If patterns suggest withdrawal or dissatisfaction, it flags the issue for review.
- Conduct Smart, Non-Intrusive Exit Interviews
AI agents can run chat-based exit interviews that feel more relaxed than formal calls. They ask meaningful questions, collect honest responses, and summarise key takeaways.
- Analyse Trends in Attrition Reasons
Over time, the agent reviews data from exit interviews, engagement feedback, and performance history to identify patterns. This helps HR leaders understand what’s causing people to leave and how to address it.
HR is just one part of the puzzle. See how AI agents are helping out in legal compliance too.
Key Benefits of AI Agents in HR
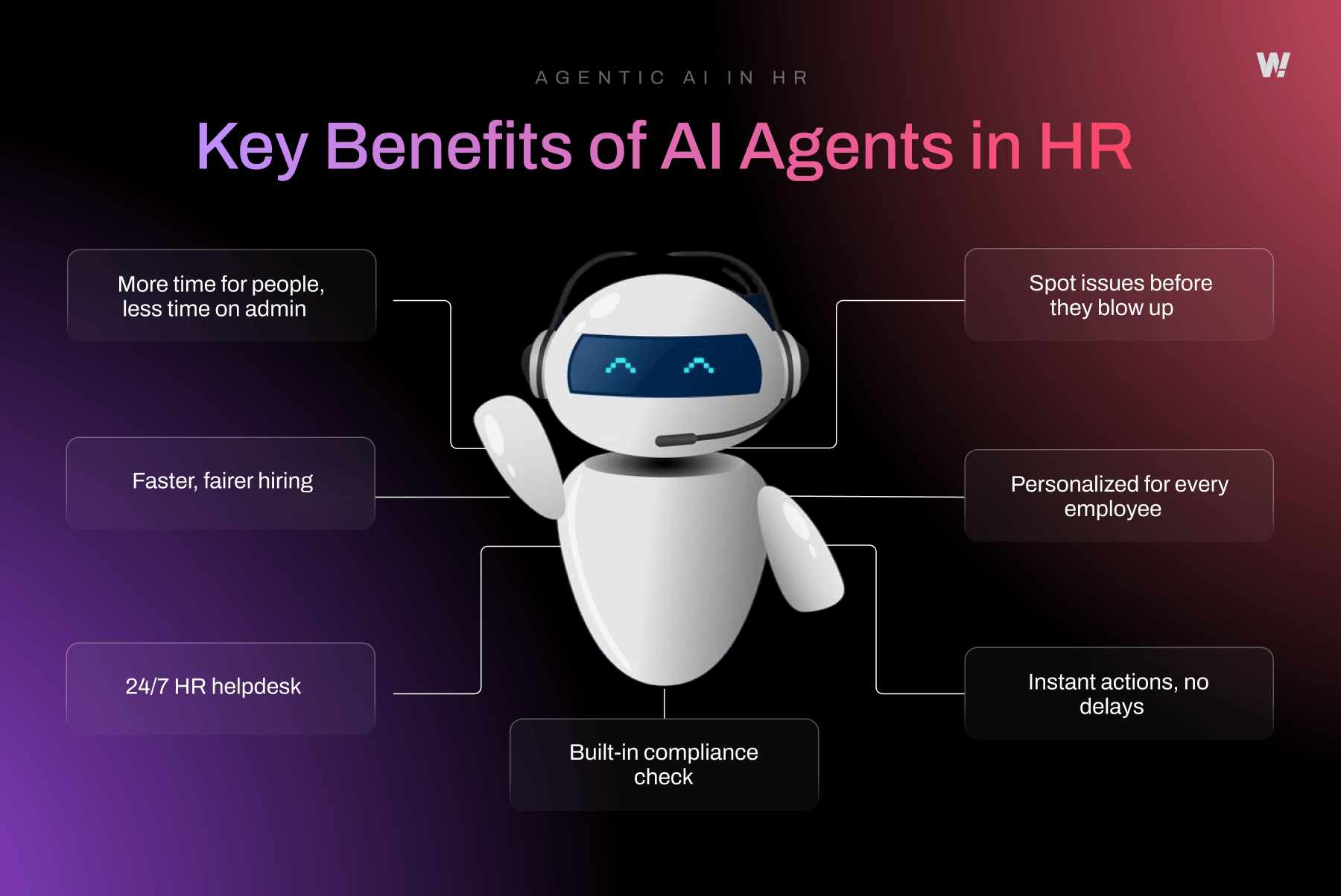
1. More Time for People, Less Time on Admin
AI agents handle repetitive and manual administrative tasks like scheduling interviews, managing emails, and updating records.
This reduces the burden of routine HR tasks and frees up time for deeper, people-first conversations.
HR teams can focus on employee well-being, culture, and strategic planning—rather than chasing paperwork.
2. Faster, Fairer Hiring
Hiring the right people quickly and fairly is easier with AI in HR.
AI agents review CVs objectively, removing unconscious bias during screening.
They match candidates to job roles instantly based on pre-set criteria, speeding up HR processes and improving talent acquisition decisions.
3. 24/7 HR Helpdesk
Employees no longer need to wait for office hours to get their questions answered.
AI agents provide round-the-clock support, answering FAQs about leave policies, payslips, and internal tools.
This improves the employee experience and reduces the load on the HR department.
4. Spot Issues Before They Blow Up
With access to sentiment data and activity trends, HR AI agents can detect signs of disengagement early.
They monitor mood, missed meetings, or survey results to flag burnout or low morale.
This allows HR leaders to take action before issues lead to attrition or performance decline.
5. Personalised for Every Employee
Every person’s needs at work are different, and AI agents adapt accordingly.
From customised onboarding plans to wellness suggestions, support is tailored to the individual.
This personalisation helps improve employee engagement and supports better employee development.
6. Instant Actions, No Delays
If it’s sending a survey, updating employee records, or sharing documents, AI agents execute tasks in real time.
There’s no waiting for approvals or backlogs information flows quickly and tasks are completed without delay.
This improves the speed and reliability of core HR operations.
7. Built-in Compliance Check
Staying compliant with policies and regulations is critical in HR.
AI agents track actions and flag issues that may break company policies or labour laws.
They ensure that every step in HR processes is logged, traceable, and ready for audits supporting compliance and risk management automatically.
Building AI Agents for HR: A Step-by-Step Guide
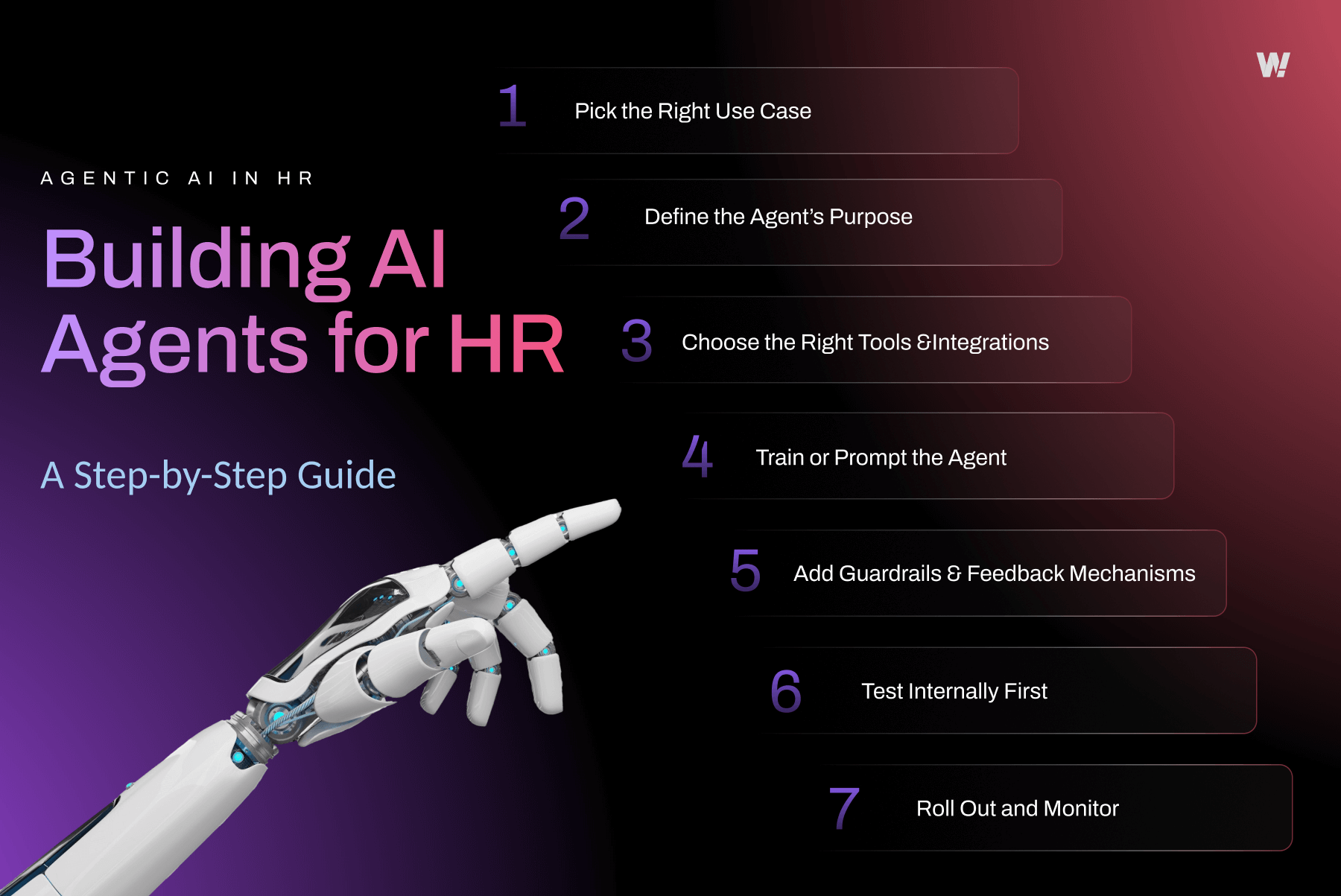
Step 1: Pick the Right Use Case
Start with a small, clearly defined task that solves a common problem in your HR workflow.
Why it matters:
A focused use case allows you to quickly test the impact of AI without disrupting your entire HR department.
Examples of good starting points:
- Screening job applications: Use an AI agent to parse and rank CVs based on job criteria.
- Answering HR FAQs: Let the agent handle frequent employee questions about leave, salary slips, or benefits.
- Sending engagement nudges: Schedule and send regular messages to check in with employees or remind them about wellness activities.
What to avoid:
Don’t start with high-risk tasks like performance review assessments or sensitive employee communications until trust and accuracy are established.
Step 2: Define the Agent’s Purpose
Every AI agent should have a clear, measurable purpose. Without a goal, it’s difficult to judge success or guide behaviour.
Ask these questions:
- What outcome do we want to achieve?
- What specific problem is the agent solving?
- How will we know it’s working?
Example purposes:
- “Reduce the average time to shortlist candidates from 3 days to 2 hours.”
- “Provide real-time answers to top 20 employee policy questions.”
- “Ensure onboarding steps are completed within the first week.”
Step 3: Choose the Right Tools and Integrations
Your AI agent is only as powerful as the tools it can access. For it to be useful in HR processes, it needs to integrate with your existing HR systems and platforms.
Common integrations include:
- ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems): To pull in job applications and update candidate status.
- HRMS platforms (e.g. SAP SuccessFactors, BambooHR): To access employee records, leave data, and payroll.
- Communication tools (Gmail, Outlook, Slack, Teams): To send updates, reminders, or engage with employees.
- Internal wikis or Notion: To access company policies and training materials.
Make sure the tools support secure APIs or connectors so the AI agent can interact with them smoothly.
Tip: Start with read-only access for safety, then gradually allow write actions (like updating records or sending emails) once tested.
Step 4: Train or Prompt the Agent
This is where the agent learns how to behave, what tone to use, what to say, and how to respond in various HR scenarios.
Two ways to do this:
- Training (for more advanced or custom agents):
Feed it documents like job descriptions, company policies, previous candidate evaluations, onboarding manuals, and sample conversations.
- Prompting (for prebuilt agents or LLM-based tools):
Write clear instructions such as:
- “Always respond in a professional, friendly tone.”
- “If asked about maternity leave, refer to policy Section 4.2.”
- “Do not answer legal questions—escalate to HR.”
Include examples of both good and bad responses so the agent can learn from context.
Goal: Build an agent that responds like a helpful and informed member of the HR team.
Step 5: Add Guardrails and Feedback Mechanisms
No AI agent should run without human oversight especially in HR, where mistakes can affect trust and compliance.
Set clear boundaries and approvals:
- Should the agent send emails directly to candidates, or just draft them for review?
- Who reviews policy answers or escalates sensitive topics?
- Can the agent update employee data, or is that limited to view-only?
Build feedback loops:
- Allow users to rate responses (“Was this helpful?”).
- Log errors or misunderstandings for review.
- Regularly review agent logs to catch trends or potential compliance gaps.
Step 6: Test Internally First
Before releasing your AI agent to the whole organisation, run it in a small test group.
Pilot group ideas:
- A few recruiters within the HR department testing hiring functions
- A small team of new joiners trying out onboarding support
- Line managers using the agent to access performance data or policy answers
What to test for:
- Does the agent understand and respond accurately?
- Are there bugs, missing data, or miscommunications?
- How do users feel about using it?
Step 7: Roll Out and Monitor
Once you’re confident in its performance, launch the agent organisation-wide. But the work doesn’t stop there.
Post-launch checklist:
- Monitor usage patterns, what’s being used most or ignored
- Review errors and agent logs weekly
- Keep your documents and prompts updated as company policies evolve
- Ask employees and HR professionals for regular feedback
Example improvements:
- Add new FAQ topics based on employee queries
- Refine how the agent filters candidates based on recruiter preferences
- Adjust the tone or format of messages based on internal style updates
Final Thoughts
AI agents in HR are making everyday work much easier. They help with tasks like sorting resumes, answering common employee questions, and managing schedules. This means HR teams don’t have to spend so much time on repetitive work.
With more time on their hands, HR professionals can focus on what really matters supporting employees, improving company culture, and making better hiring decisions. AI agents aren’t here to replace people, they’re here to help them do their jobs better.
Partner with Agentic AI Labz
At Agentic AI Labz, we specialize in developing next-generation AI agents made for real-world enterprise challenges. Whether you’re exploring workflow automation, predictive intelligence, or customer-facing agents, our team brings deep expertise and cutting-edge platforms to the table.
Ready to begin your AI agent journey?
Partner with Agentic AI Labz to unlock measurable ROI, future-proof operations, and lead with intelligence.